Educational objectives:
1. To develop a Patient-reported outcome measures (PROM) to assess disease activity in microscopic colitis (MC) fulfilling the requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The European Microscopic Colitis Activity Index (E-MCAI) was developed in four steps: 1) A list of symptoms associated with active MC was created by a group of experts in the field. 2) Content validity of the symptoms was performed by experts (n=14) and patients (n=79) using the Content Validity Index. 3) Questions and response alternatives were created for each symptom, and validity of the E-MCAI was evaluated with cognitive interviews with patients (n=7) and by the experts. 4) A pilot postal survey was performed to ensure usability.
Seven of the symptoms related to active MC fulfilled the criteria for content validity and were included in the E-MCAI: stool consistency, stool frequency, stools at night, feel a need to pass more stools shortly after a bowel movement, urgent need to empty the bowel, leakage of stool, and abdominal pain. The development and validation process resulted in the current version of the E-MCAI consisting of six questions related to MC.
The E-MCAI was developed using the methods advocated by the FDA. The evaluation indicates good content validity. Further evaluation will be performed to accomplish construct validity, reliability, and responsiveness in future cross-sectional and longitudinal studies.
Educational objectives:
1. To develop a Patient-reported outcome measures (PROM) to assess disease activity in microscopic colitis (MC) fulfilling the requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The European Microscopic Colitis Activity Index (E-MCAI) was developed in four steps: 1) A list of symptoms associated with active MC was created by a group of experts in the field. 2) Content validity of the symptoms was performed by experts (n=14) and patients (n=79) using the Content Validity Index. 3) Questions and response alternatives were created for each symptom, and validity of the E-MCAI was evaluated with cognitive interviews with patients (n=7) and by the experts. 4) A pilot postal survey was performed to ensure usability.
Seven of the symptoms related to active MC fulfilled the criteria for content validity and were included in the E-MCAI: stool consistency, stool frequency, stools at night, feel a need to pass more stools shortly after a bowel movement, urgent need to empty the bowel, leakage of stool, and abdominal pain. The development and validation process resulted in the current version of the E-MCAI consisting of six questions related to MC.
The E-MCAI was developed using the methods advocated by the FDA. The evaluation indicates good content validity. Further evaluation will be performed to accomplish construct validity, reliability, and responsiveness in future cross-sectional and longitudinal studies.
Educational objectives:
- To know the main nursing intervention in caring and management of patients with IBD
- To review the evidence about the impact of these interventions on patients' outcomes
- To have an overview of the methodology that will be used in this project: the network meta-analysis
Summary:
Specialist nurses dedicated to the care and management of patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) are increasing in number and roles across Europe. Despite the increased interest in the opportunities connected to this emerging healthcare professional, both from patients’ and clinicians’ perspectives, scarce evidence is available on the effectiveness of specialist nursing interventions. A deep review of the impact of specialist nursing interventions on the management and care of patients with IBD, especially on their health-related (HR) quality of life (QoL), is needed.
The main aim of this project is to systematically review studies assessing the impact of specialist nursing interventions in improving care and management of IBD patients and their QoL.
This project also aims to:
- identify which skills and types of nursing interventions should be developed to respond more effectively to patients' health needs;
- assess the effects of nursing interventions also on different outcomes such as (i) the proportion of patients entering remission, (ii) the proportion of patients in whom remission is maintained, (iii) the duration of remission, (iv) patients’ compliance and satisfaction, (v) number/rate of hospital admissions, (vi) costs savings.
These objectives will be reached through the conduction of a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
With the grant of the NECCO we started at the Erasmus MC sophia children's hospital a multicenter study into validation of the Transition Success Score (TSS). The TSS was developed using an international Delphi procedure (van den Brink; 2019). Hopefully after this validation study the TSS can be used to measure the success/failure of transition in care.
Data from Phase 3 studies in Crohn’s disease (CD) demonstrated significant improvements in endoscopic outcomes with risankizumab (RZB) versus placebo (PBO) following 12-weeks (wks) induction therapy. Continued maintenance therapy with 360mg RZB SC led to significantly higher rates of endoscopic response and remission at Wk52 compared to withdrawal/placebo. This post-hoc analysis examined the durability of SC RZB maintenance therapy for endoscopic outcomes among patients achieving these endpoints at the end of induction
MethodsPatients achieving clinical response with 12-wks IV RZB induction therapy in ADVANCE or MOTIVATE entered the maintenance study, FORTIFY, and received either RZB SC or had RZB withdrawn and received placebo for 52 wks. Forthis analysis, endoscopic outcomes in the RZB 360 mg SC (N=141) and withdrawal/placebo (N=164) arms are reported. Maintenance of endoscopic response, endoscopic remission, and/or an SES-CD score of 0-2 were assessed at Wk52 in patients who achieved these endpoints at Wk0 of maintenance (Wk12 of induction). Safety was assessed throughout the study.
ResultsFollowing 12-wks of IV RZB induction therapy (FORTIFY Wk0), 141 patients were randomized to RZB 360 mg (patients achieving endoscopic response, 55/141; endoscopic remission, 39/141; SES-CD score of 0-2, 29/141) and 164 were randomized to withdrawal (PBO SC) (patients achieving endoscopic response, 73/164; endoscopic remission, 46/164; SES-CD 0-2, 32/164). Maintenance of endoscopic response at Wk52 was demonstrated in 70.2% (39/55) of patients receiving RZB 360 mg SC versus 38.4% (28/73) of patients in the withdrawal (PBO SC) arm (P<0.001). Maintenance of endoscopic remission at Wk52 was demonstrated in 74.4% (29/39) of patients receiving RZB 360 mg versus 23.9% (11/46) of patients in the withdrawal (PBO SC) arm (P<0.001). Maintenance of an SES-CD score from 0-2 at Wk52 was demonstrated in 65.5% (19/29) of patients receiving RZB 360 mg versus 21.9% (7/32) of patients in the withdrawal (PBO SC) arm (P<0.001).RZB maintenance treatment was well-tolerated and no new safety signals were observed. The safety profile of RZB has been reported previously.1–5
RZB IV induction followed by SC maintenance therapy led to sustained improvements in endoscopic outcomes, demonstrating the durability of efficacy with continued RZB treatment in patients with moderate to severe CD.
References:
1 Feagan, B. G. et al.Lancet 389, 1699–1709 (2017) 2 Feagan, B. G. et al.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3, 671–680 (2018) 3 Ferrante, M. et al.Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis jjab093 (2021) 4 Ferrante, M. et al. in UEGW 2021 5 D’Haens, G. et al. in DDW 2021
We used the postoperative recurrence model to better understand the role of AIEC bacteria in Crohn’s disease (CD), taking advantage of a well-characterized postoperative cohort.
MethodsFrom the REMIND prospective, multicenter cohort of operated CD patients (ileocolonic resection), AIEC identification was performed within the surgical specimen (M0) (N=181 patients) and the neo-terminal ileum (n=119 patients/181) during colonoscopy performed 6 months after surgery (M6). Endoscopic postoperative recurrence was graded using Rutgeerts’ index, which was interpreted, either from a clinical point of view (postoperative endoscopic recurrence ≥ i2b or severe ≥ i3), or from a pathophysiological point of view (reappearance of the first ileal lesions = i1 and more advanced postoperative ileal recurrence = i2b + i3). The mucosa-associated microbiota was analyzed by 16S sequencing at M0 and M6. Relative risks (RR) or odds ratios (OR) were adjusted on potential confounders ((gender, smoking, CD duration, CD phenotype, prior bowel resection, indication for surgery, granuloma, preventive treatment, antibiotics).
ResultsAmong the 228 patients included at the time of the analyzes, the search for AIEC was carried out in 181 patients at M0, and 119 patients at M6. Among these 181 patients included in our study, 46.3% did not receive any preventive treatment for endoscopic postoperative endoscopic recurrence while 24.3% have been treated with anti-TNF to prevent postoperative recurrence.
AIEC prevalence was two-fold higher within the neo-terminal ileum at M6 (30.3%) than within the surgical specimen (14.9%) (p<0.001). AIEC within the neo-terminal ileum at M6 was associated with higher rate of early ileal lesions (i1) (41.6% vs 17.1%; aRR=3.49[1.01-12.04], p=0.048) or ileal lesions (i2b + i3) (38.2% vs 17.1%; aRR=3.45[1.06-11.30], p=0.040) compared to no lesion (i0). AIEC within the surgical specimen was predictive of higher risk of i2b-endoscopic POR (aOR=2.54[1.01-6.44], p=0.049) and severe endoscopic POR (aOR=3.36 [1.25-9.06], p=0.017). While only 5.0% (6/119) of the patients were AIEC-positive at both M0 and M6, 43.7% (52/119), patients with history of AIEC infection (M0 or M6) had higher risk of ileal endoscopic POR (aOR=2.32 [1.01-5.39], p=0.048]), i2b-endoscopic postoperative recurrence (aOR = 2.41[1.01-5.74]; p=0.048) and severe endoscopic postoperative (aOR = 3.84[1.32-11.18], p=0.013). AIEC colonization was associated with a specific microbiota signature including increased abundance of Ruminococcus gnavus.
ConclusionBased on the postoperative recurrence model, our data support the role of AIEC in the early steps of ileal CD.
The educational objectives of the presentation are:
1. To understand that the choice of long-term treatment of IBD must take into account the benefit-risk balance of old and new IBD drugs
2. To review the most important aspects of IBD drug-induced cancers and serious infections
3. To understand that in most cases benefits outweigh risks, and that patients should not be undertreated
4. To understand, based on the example of tofacitinib, that it is important keep prudent with recently approved IBD drugs until powered data is available
After introducing the concept of benefit-risk balance, the presentation will review the three major aspects of IBD drug potential complications: drug-class specific complications, malignancies, and serious infections, including opportunistic infections. A special focus will be made on thiopurine-induced lymphomas, thiopurine and anti-TNF-induced serious bacterial and viral infections, and how to manage these risks. We will then discuss the difficult choice of immunosuppressants in frail and older patients, based on drug-class specific safety data. Finally, using the example of tofacitinib, we will illustrate the importance of prescribing with caution recently approved drugs, until we have extensive safety data.
Educational objectives:
1. To understand the ultrasound features that represent disease activity in CD and UC
2. To get an overview of existing activity scores in CD and UC
3. To get an overview of transmural healing
4. To know the advantages and challenges by applying activity scores.
Previous studies suggested a role for segmental colectomy (SC) and total colectomy (TC) for colonic Crohn’s disease (cCD). TC might reduce recurrence rates, at the cost of impaired quality of life and higher stoma rates. We compared the long-term outcomes of SC and TC.
MethodsThis is an international, multicentric study on data from the prospective databases of six centres. All consecutive patients operated on between 2000 and 2019 for cCD with SC or TC were included. Exclusion criteria were colorectal cancer, previous bowel resections, and lack of follow-up data. Disease extension was based on involvement of 1 to 5 colonic segments. Resection of 1-3 segments was classified as SC, resection of 4-5 segments as TC. Primary aim was surgical recurrence after SC vs TC. Secondary aims were perioperative complications, stoma formation rate, and predictors of recurrence.
ResultsData of 687 (56.2% women) patients were analysed. Mean age at diagnosis and at surgery were 30±15.8 and 40.4±15.4 years. Disease duration was 10.4 ± 8.6 years. 16.6% of patients were A1, whereas most (62.2%) were diagnosed between 17 and 40 years. Isolated cCD (L2) was present in 61.1%, ileocolic CD (L3) in 38.9%, and concomitant jejuno-ileal CD (L4) in 3.2%. Most had stricturing (B2) cCD (41.9%). Active perianal disease was found in 28.9% patients. SC was performed in 285 patients, TC in 402. The latter more frequently had isolated cCD, inflammatory (B1) disease, current (37.8 vs 16.5%, p<0.001) or previous (56 vs 32.6%, p<0.001) perianal CD, and longer disease duration (11.3 ± 8.9 vs 9.2 ± 7.9, p<0.001). Postoperative complications and mortality were similar, but TC patients more frequently required 90-day readmission (6% vs 2.1%, p=0.02). Temporary (31.6 vs 21.4%, p<0.001) and definitive (39.3vs8%, p<0.001) stomas were more likely after TC. The 15-year cumulative surgical recurrence was 36%, more likely in the TC group (44 vs 27%, Log-Rank p=0.006), and it was not affected by the number of colonic segments involved (23 vs 28%, 1-3 vs 4-5 segments p=0.2) (Fig 1). In patients with 1-3 segments involved, postoperative treatment with biologics, compared to any other regimen, reduced the risk of recurrence (25 vs 51%, p<0.001), while early age at diagnosis (p=0.02) and perianal CD (p=0.01) increased the risk. Omission of biological therapy (HR 5.4, 95%CI 5.1-5.8 p<0.001), and paediatric diagnosis (HR 2.1, 95%CI 2.3-3.1 p<0.001) were the strongest predictors of recurrence in this subgroup.
In this study, SC was safe, required less frequently stoma and repeated surgery, compared with TC. These findings question previous data on the topic and might be supported by the efficacy of postoperative biologic therapy on cCD.
The world wide web and social media platforms have become an unprecedented source for sharing self-experience, potentially allowing the collection and integration of health data with patient experience
MethodsStuffThatWorks (STW) is an online open platform that applies machine learning and the power of crowdsourcing where patients with chronic medical conditions can self-report and compare their individual outcomes using a structured online questionnaire. The present study analyzed de-identified self-reported personalized comparative treatments' effectiveness for CD. The design was a cross-sectional, international, crowdsourcing, questionnaire and AI web-based study of patients with Crohn's self-reporting their outcomes by 06/11/21. A proprietary STW Bayesian inference model was built to measures the level of improvement in condition severity and clinical indicators for each treatment and ranks treatment effectiveness. A linear regression model was used to examine co-variate association with the current condition severity as the outcome. Finally, the effectiveness of first-line biological treatments was analyzed by multiple treatment comparisons model and by calculating odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals for each treatment pair.
ResultsA total of 5898 self-reported CD patients were included for the analysis. Most participants were female (76.13%) and from English speaking countries (91%). Overall, anti TNF drugs were the most reported tried treatment (71.97%) followed by steroids (46.22%) and diet (43.8%). Among Biologic therapy (BT) tried by STW CD users, Infliximab (IFX) and Adalimumab (ADA) were ranked most effective by the STW effectiveness model, by change in condition severity on 1-5 scale (mean change of 1.19 points, estimated lower-upper bounds 1.10-1.28), followed by Ustekinumab (UST) (mean 1.07, bounds 0.88-1.26), and Vedolizumab (VDZ) (mean 0.96, bounds 0.74-1.17). Bowel surgery (mean 1.19, bounds 0.98-1.40), and cannabis (mean 1.01, bounds 0.72-1.31) were also among the top 5 most effective treatments together with BT. The odds ratio was calculated for each BT pair, with IFX more effective than ADA, UST and VDZ (OR 2.34 (CI 1.88 – 2.80), 3.08 (CI 2.44 – 3,73), 7.16 (CI 6.53 – 7.80), respectively), ADA more effective than UST and VDZ (OR 1.32 (CI 0.74 - 1.9), 3.06 (CI 2.49 - 3.63), respectively), and UST more effective than VDZ (OR 2.32 (CI 1.6 - 3.05)).
ConclusionWe present the first online crowdsourcing platform-based study of treatment self-reported outcomes in CD. Net-based crowdsourcing patient-reported outcomes' platforms can potentially help both clinicians and patients select the best treatment for their condition.
An association between shorter disease duration and improved clinical efficacy has been shown in post hoc analyses of clinical trial data with biological therapies in Crohn’s disease (CD). The efficacy and safety of risankizumab (RZB) as induction and maintenance therapy have been recently reported. Here, the efficacy of RZB stratified by baseline CD duration is reported.
MethodsIn ADVANCE (NCT03105128) and MOTIVATE (NCT03104413), patients with moderately to severely active CD received intravenous (IV) RZB induction therapy or placebo (PBO) for 12 weeks. Patients with clinical response to RZB IV induction were re-randomised in a 52-week maintenance study (FORTIFY, NCT03105102) to receive subcutaneous (SC) RZB or PBO (ie, withdrawal). For this post-hoc analysis, patient subgroups were stratified by years of CD duration at baseline (< 2, 2–5, > 5–10, and > 10 years). Induction analyses focused on patients who received RZB 600 mg IV or PBO for 12 weeks. As all patients who entered maintenance responded to RZB IV induction, maintenance analyses were limited to those patients who responded to induction and then received RZB 360 mg SC for 52 weeks. Clinical and endoscopic outcomes were evaluated using nonresponder imputation incorporating multiple imputation to handle missing data due to impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Safety was assessed throughout the studies.
ResultsThe induction and maintenance analyses included 527 patients who received RZB 600 mg IV and 141 patients who received RZB 360 mg SC, respectively. At the end of induction (week 12), patients with CD duration of < 2 years achieved higher rates of endoscopic outcomes with IV RZB induction vs patients with longer durations of disease (Figure 1), and regardless of baseline CD duration, greater proportions of RZB-treated patients achieved clinical remission (defined by stool frequency and abdominal pain), endoscopic response, endoscopic remission, and ulcer-free endoscopy vs PBO (P ≤ .05). Clinical remission rates at week 12 were numerically higher in patients with CD duration of < 5 years vs > 5 years (Figure 1). Similar results for improved clinical and endoscopic outcomes associated with shorter disease duration were observed at week 52 with RZB 360 mg SC maintenance treatment (Figure 2). RZB was well tolerated with lower rates of serious adverse events and serious infections vs PBO in induction, across CD duration subgroups.

RZB induction and maintenance therapy was effective and well tolerated with a safety profile generally similar across CD duration subgroups. Achievement of clinical and endoscopic endpoints were higher in patients with shorter duration of CD, suggesting that earlier introduction of RZB therapy may lead to improved outcomes.
Vedolizumab (VDZ), a monoclonal antibody that targets α4β7 integrin, was approved to treat moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis (UC) based on the presumption that it blocks T cell recruitment to the inflamed intestinal mucosa. The clinical evidence suggests that up to 50% of UC patients do not achieve disease remission under VDZ treatment. This study aims to identify changes in cell abundances and molecular pathways associated with VDZ response in UC. To this end, we included anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF)-naïve and anti-TNF-exposed patients with active UC, and utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) and high-dimensional flow cytometry (Cytek) to assess the peripheral blood and the gut mucosal compartments.
MethodsGut mucosal biopsies from inflamed and non-inflamed regions, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were obtained from UC patients 2 wks before (t0) and 14 wks after (t4) the start of VDZ administration. Response to treatment was prospectively evaluated based on endoscopic assessment (defined as a decrease in total Mayo score between t0 and t4) and physician global assessment (PGA) that incorporates disease activity score and biochemical measurements.
A total of 25 UC patients (pts) were included: 44% anti-TNF-naïve. Endoscopic response to VDZ was observed in 32% of UC pts, while 56% of pts showed response based on PGA. The VDZ response rate (by PGA) was higher in anti-TNF-naïve pts vs anti-TNF-exposed pts (82% vs 36% responders, respectively). A preliminary analysis was performed on samples from 8 (out of 25) UC pts, profiling >70,000 gut mucosal cells and >25,000 PBMCs. Within the mucosal compartment, at t0 we identified immune cells (50% of all captured cells), stromal cells (10%), and epithelial cells (40%). Upon inflammation, the proportion of immune cells increased to 70%, stromal cells to 20%, while epithelial cells depleted to 10%. Notably, all main identified immune cell lineages – T cells, B cells and myeloid cells – contributed to the expansion of the immune cell compartment in inflamed mucosa. In line with scRNAseq data, we identified all major immune cell populations and detected expression of both the classic gut-directed and the redundant trafficking integrins by Cytek.
ConclusionThe preliminary results substantiate our current understanding of VDZ biology in UC. We confirm that anti-TNF-naïve pts have a higher response rate to VDZ vs anti-TNF-exposed pts. With this unique cohort, our study has the power to further explore molecular mechanisms and pathways that underlie VDZ response at the single-cell level.
Non melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) is amongst the most common cancers worldwide and the incidence of both melanoma and NMSC is still rising. This is not only due to people reaching an older age, but also to the increasing amount of people receiving immunosuppressive medication. While immunosuppression in organ transplant patients serves as the most well-known model for these iatrogenic induced skin cancers, alternative forms of immunomodulating therapies, such as the biologicals, also caught attention because of their potential to disrupt skin cancer immunosurveillance. Data on biologicals, with anti-TNFα most studied, are more controversial, however, and diverge according to the inflammatory disease (Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), psoriasis or rheumatoid arthritis) for which they are given.
In IBD patients there is an elevated risk for both NMSC as well as melanoma. Whereas NMSC in IBD patients seems associated with current or past use of thiopurines, it is still unclear if the higher risk for melanoma in IBD patients can be attributed to the use of TNF inhibitors. As the cutaneous malignancies in these immunosuppressed patients behave often more aggressively, preventive strategies are mainstay in the approach of skin care, requiring good coordination between the gastroenterologist and the dermatologist. For IBD patients with a present or past history of a cutaneous malignancy, a multidisciplinary care involving the gastroenterologist and dermatologic or oncologic specialties will have to guarantee the balance between the IBD treatment and the management of the malignancy when facing challenges as maintaining local tumour control, avoiding cancer recurrence/new cancer with future IBD treatment or dealing with checkpoint-inhibitor colitis during management of advanced or metastatic skin cancer.1. To learn about the epidemiology of Small Bowel Adenocarcinoma.
2. To understand the absolute risk and relative risk linked to it.
3. To review practical management of Dysplasia/ SBA
Educational objectives
To discuss the evidence for somatic mutation in the IBD affected colonic epithelium
To consider mechanisms mutagenesis
To discuss evidence for selection pressures on mutations and their implications for cancer risk and inflammation
1. To identify the areas where standardisation of IBD pathology reporting is achievable and the areas requiring improvement.
2. To recognise the importance of a multidiscipinary approach and good communication.
3. To consider the development of a consistent approach to the assessment and description of IBD histology.
4. To be aware of the diversity of approaches to the assessment of histological acitvity.
4. To explore the ideal ways in which to construct the summary and conclusion of an IBD pathology report.
5. To be aware of the existence and value of guidelines and datasets in pathology generally and in IBD pathology in particular.
Four randomized controlled trials studying faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in active UC patients showed variable success rates. The efficacy of FMT appears to be influenced by various factors including donor- and procedure-specific characteristics. We hypothesized that the outcome of FMT in patients with active UC could be improved by donor preselection on microbiota level, by using a strict anaerobic approach, and by repeated FMT administration.
MethodsThe RESTORE-UC trial (NCT03110289) was a national, multi-centric double-blind, sham-controlled randomized trial. Active UC patients (Total Mayo score 4-10 with endoscopic sub-score ≥2) were randomly allocated (1:1) to receive 4 anaerobic-prepared superdonor (S) FMT or autologous (A) FMT (Figure 1) by permutated blocks (2 and 4) and stratified for weight, concomitant steroid use, and therapy refractoriness.
S-FMTs were selected after a rigorous screening excluding samples with Bacteroides2 enterotype, high abundances of Fusobacterium, Escherichia coli and Veillonella and the lowest microbial loads (Q1).
A futility analysis after 66% (n=72) of inclusions was planned per protocol including a modified intention-to-treat (mITT) analysis using non-responder imputation (NRI) for patients receiving at least one FMT. The primary endpoint was steroid-free clinical remission (Total Mayo ≤ 2, with no sub-score >1) at week 8.
Between March 2017-2021, 72 patients signed the ICF and 66 were randomly allocated to S-FMT (n=30) or A-FMT (n=36) and received at least one FMT. In the S-FMT and the A-FMT resp. 4 and 5 patients terminated the trial early due to worsening of colitis (4 in both arms) or FMT enema intolerance (1 A-FMT). They were included in the mITT analysis using NRI (Fig. 2). Both study arms were matched for baseline characteristics (Table 1), yet a trend (p= 0.066) towards higher concomitant biological use in the S-FMT arm was observed.
After 66% of intended inclusions, the primary endpoint was reached in 3/30 (10%) S-FMT and 5/31 (13.9%) patients randomized to A-FMT (p=0.72).
As the predefined minimum difference between both treatment arms was not attained, the study was stopped due to futility. The full set of endpoints are summarized in Table 2.Of note, no patients on concomitant biologicals reached the primary endpoint.
There were 2 serious adverse events in the A-FMT arm: dysuria requiring hospitalization and worsening of UC requiring colectomy.


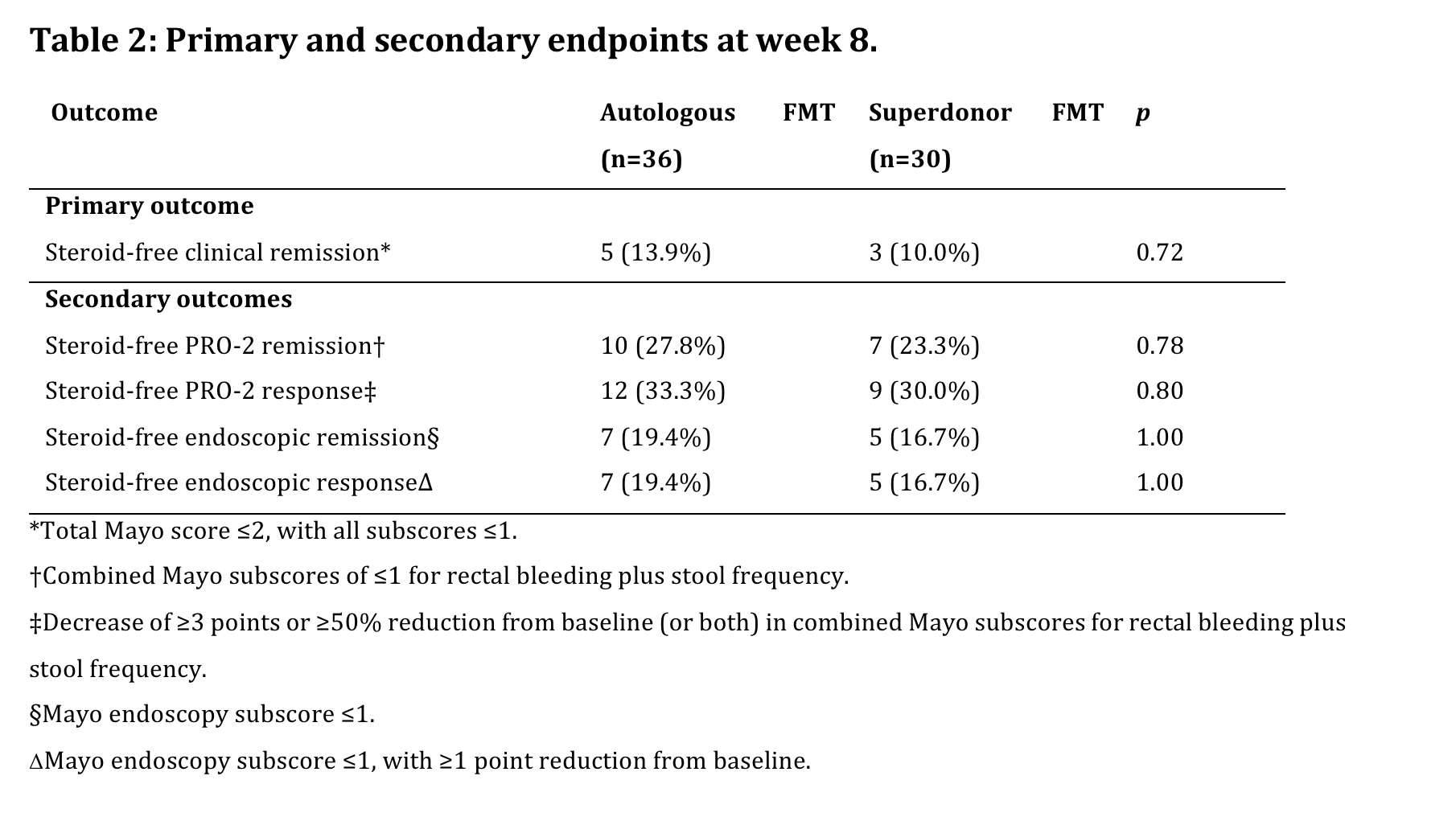
In this double-blind sham-controlled trial comparing repeated administrations of anaerobic-prepared S-FMT with A-FMT in patients with active UC, no significant difference in steroid-free remission rates at week 8 were observed. The FMT procedure was generally well tolerated, and no new safety signals were observed.
