1. To define the appropriate timing between medical and surgical management of IBD
2. To review medical and surgical treatment indications of the complications of IBD
3. To learn how to decide in multidisciplinary team between the two modalities of treatment
This presentation will focus on how to identify risks for surgical complications in surgery for inflammatory bowel disease, as well as how to decrease the risk prior to surgery. There will also be a discussion on how to act when surgical complications have developed, as this risk is increased compared to colorectal surgery in general.
Educational objectives:
1. To review when to perform surgical resection in CD, as illustrated with a patient journey with limited L1 Crohn's disease
2. To get an insight into the surgical procedure via video presentation
3. To summarize literature on risk-stratification, the importance of proactive monitoring and individual treatments for postoperative recurrence
1. to understand when and why surgery is indicated in selected patients with UC
2. to review the different surgical options in patient operated for ulcerative colitis
3. to precise the consequences for the patient in terme of function, quality of life and follow up, after surgery for UC, according to the operation performed
4. to have an overwiew of the best way to follow a patient after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for ulcerative colitis
5/ to review the possible problems occurring during follow up up of patients after ileal pouch-anal anastomosis and the treatment for each problem
Discussion about incidence of colorectal cancer, small bowel cancer, and anal cancer in IBD with a focus on surgical strategies
IBD and cancer: surgical strategy in UC
Educational objectives:
- To emphasise that cancer risk is depending on patient and disease characteristics, and varies with duration of disease
- To review the incidence of CRC rate in colectomy specimens over the last decades
- Give an overview of surgical approaches in case of UC malignancy and discuss ongoing controversies (proctocolectomy vs segmental resection/ pouch or not/ mucosectomy/ impact of (neo)-adjuvant therapy)
Educational objectives:
1. To understand the concept of tailored medical therapy in ulcerative colitis 'the right therapy to the right patient at the right time' on the basis of an individual patient’s biology and possible prognostic factors
Treatment algorithms will be presented for different disease presentations of ulcerative colitis.
Therapeutic drug monitoring will be discussed and the future options of tailored medicine will be discussed.
Robust and sensitive therapeutic targets are key in effective management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease1. Mesenteric hyperaemia is a recognized sign of active disease and in cross-sectional image is described as the comb sign. Although it is subjectively described, no automated quantitative MRI-based measures have been developed.
We aim to develop an automated methodology using contrast-less time of flight (TOF) Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA).
MethodsA MATLAB algorithm was developed to track the vessels on a 3D maximum intensity projection of a TOF MRA data set and calculate an arborization Index which is the number of branching points in the intrabdominal vessels (figure 1). 2D TOF scans were acquired in the transverse plane between the top of the hip joint and L4 vertebra using a 3T Ingenia Wide bore scanner (Philips, The Netherlands). The primary outcome was a comparison of the arborization index between Crohn’s disease (CD) and healthy volunteers (HV) groups. A planned sub-analysis was undertaken across CD and HV matched for BMI to investigate the effect of visceral fat on the arborization index. Repeated measures were undertaken to evaluate the variability of the quantification method. No contrast agents were used for the TOF MRA scans. Biological variations within each group and test-retest repeatability were assessed using the coefficient of variation (CV). Statistical analysis with unpaired, two-tailed t-tests were conducted and differences were considered significant when the p-value ≤0.05. All absolute values are presented as mean ±standard deviation (SD).
In this prospective pilot study, 7 CD patients (C-Reactive Protein=5.2±6.1 mg/L, Faecal Calprotectin 611±981μg/g, BMI=23±3 kg/m2) and 15 HVs (BMI=29±7 kg/m2) were recruited. Patients showed a significantly higher arborization index when compared to HVs (mean arborization in HV=94±21 and CD=139±26; p-value=0.002). The difference in arborization index persisted in a sub-analysis of 7 HVs (BMI=24±2 kg/m2) and 7 CD patients (mean arborization in matched HVs=101±22 vs mean index in CD=139±26; p=0.01) (Figure 2). The CV was 23% for HVs and 18% for CD indicating biological variation. Test-retest variability calculated from multiple TOF scans of the same subjects gave a mean CV of 6±5% for both groups combined.
Our preliminary data suggest that the arborization index may be a useful measure of hypervascularity and hence intestinal inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Further validation to standard disease activity measures is needed across larger cohorts to better investigate the utility of this potential biomarker as a non-invasive measure of disease activity and its reversibility to IBD therapies.
1.Turner,D.,et al.Gastro.2021;160(5):1570-1583.
To clarify the risk of lymphoma in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) exposed to anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) and/or thiopurines we aimed to evaluate the Israeli IBD population.
MethodsA nested case-control study on the epidemiology cohort of the Israeli IBD Research Nucleus (epi-IIRN) including all 4 Health Maintenance Organizations in Israel linked to the Israeli Cancer Registry. Patients diagnosed since 1.1.2005 until 31.12.2015 (42,954 patients) were included and followed until 31.12.2017. Each lymphoma case was matched to 30 non-lymphoma IBD patients by age, gender, IBD subtype, and date of earliest evidence of IBD in the database. Patients with other risk factors for lymphoma, or lymphoma diagnosis prior to IBD diagnosis were excluded (figure 1). Conditional logistic regression was used to compute the association of drug exposure (anti-TNF, thiopurines and combination) with diagnosis of lymphoma. Patients without exposure to anti-TNF and/or thiopurines in each group served as reference within each group. Additionally, sub-group analyses by gender, age group at inclusion (≤48, 49-64, ≥65), time from last drug exposure (≤90 days, 91-365 days, >365 days) were done.
The final nested cohort included 5556 IBD patients (185 lymphoma cases matched to 5,371 without lymphoma). Mean follow-up (F/U): 5.5±3.5 years, 50% with Crohn’s disease, mean age at database entry 52.6±17.80 years. Anti-TNF-only exposure was documented in 4.3% (8/185) of lymphoma cases vs. 2.6% (145/5,371) of controls OR 1.97, CI 0.93-4.16, p=0.07; in males the ORs were 2.84 (CI 1.17-6.92 p=0.04) and increased to OR 3.48 (CI 1.55-7.88, p=0.002) for males <48 years and OR 2.87 (CI 1.53-5.37, p=0.001) for patients with last exposure ≤90 days (figure 2). Exposure to combination anti-TNF+thiopurines occurred in 8.6% (16/185) of lymphoma cases vs. 5.3% (282/5,371) of controls OR 2.09 (CI 1.17-3.73, p=0.013). Males on anti-TNF-thiopurine combination had OR of 3.42 (CI 1.37-8.52, p=0.003) and in sequential (non-overlapping exposure to both thiopurines and anti-TNFs during F/U) combination an OR of 2.74 (CI 1.02-7.35 p=0.02). Thiopurine-only exposure occurred in 15.1% (28/185) of lymphoma cases vs. 13.5% (726/5,371) of controls, OR 1.32 (CI 0.86-2.03, p=0.20). Males on thiopurines had an OR of 1.75 (CI 1.02-2.99, p=0.05). The risk increased further in males <48 years OR 2.17 (CI 1.01-4.66, p=0.047) and in males aged≥65 OR 3.50 (CI 1.55-7.82, p=0.002). Females were not at risk for lymphoma (figure 3).

This nationwide study suggests that exposure to anti-TNF therapy alone or in combination with thiopurines may be associated with an increased risk of lymphoma, but only in males, especially when last exposure occurred within 90 days.
Breastmilk (BM) is a complex fluid that contributes to shaping the immune system of the offspring. BM composition depends on stage of lactation, maternal health status and diet, environment, and genetics. Limited data exists on the composition of the BM from women with IBD and its potential impact on the newborn’s microbiome composition.
MethodsThe MECONIUM (Exploring MEChanisms Of disease traNsmission In Utero through the Microbiome) study is a prospective cohort study including pregnant women with IBD, pregnant healthy control (HC), and their offspring. BM samples were collected 2 weeks post-delivery. Stool samples from the offspring were collected throughout the first 3 years of life and used to assess faecal calprotectin (fCal) and gut microbiota composition (16S). Targeted proteomics of the BM samples was performed with the Olink inflammation panel (92 protein biomarkers). Correlations between specific proteins in the BM, fCal and 16S were assessed using non-parametric tests. Multiple testing correction was performed with false discovery rate (FDR). MaAsLin2 R package was used for multivariate testing.
Results236 BM samples were analysed: 174 from HC, 37 Crohn’s disease (CD), 25 ulcerative colitis (UC). Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), a cytokine with an important role in the maturation of T cells, was significantly lower in BM of women with IBD vs HC (FDR p=0.0017). The levels of TSLP in the BM of the mothers correlated negatively with infant fCal at year1 (rho=-0.20, p=0.01), and with the relative abundance of Cronobacter (MaAsLin2 FDR 0.1) of the offspring at month 1. Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (CCL20), which acts in chemotaxis of dendritic cells and T-cells and B-cells, was also significantly lower in women with CD vs HC (FDR 0.013) and in women with CD vs UC (p=0.014). Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), a collagenase involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix, was also lower in BM of women with CD (p=0.009) and a negative correlation was observed between the levels of MMP1 and fCal at 3 months and 1 year (rho=-0.20 and -0.18, p=0.01 and 0.02, respectively). Osteoprotegerin (OPG), higher in BM of women with UC (p=0.018), was positively correlated with Streptococcus (MaAsLin2 FDR p=0.2) and negatively correlated with Bacteroides and Parabacteroides (MaAsLin2 FDR p=0.03 and 0.1) in the offspring at month 1.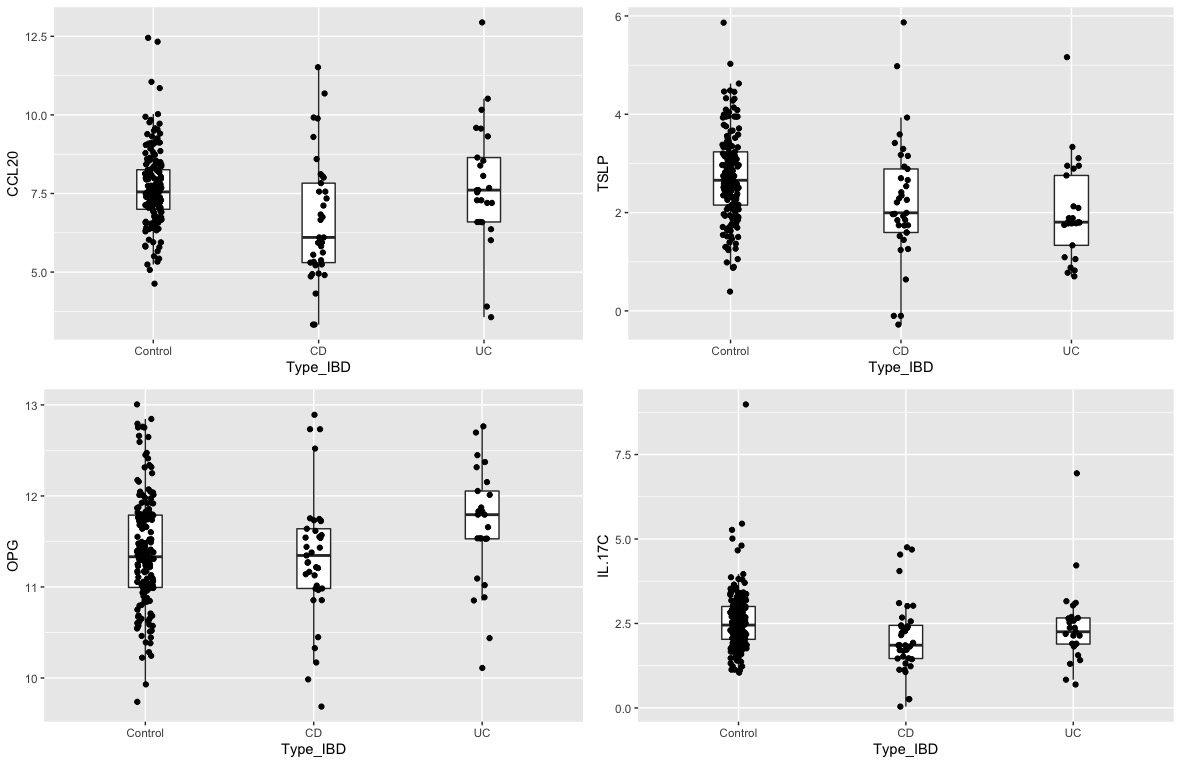
The proteomic profile of BM of women with IBD is distinct from that of women without IBD. BM composition may influence offspring’s’ gut microbiome signatures and fCal level at different timepoints. These findings suggest that BM composition may impact the offspring’s intestinal immune system maturation and microbiome development, and warrant further research.
Abdominal pain (AP), bowel urgency (BU), and fatigue are debilitating symptoms that reduce quality of life in patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). Results from two Phase 3 induction trials (U‑ACHIEVE induction [NCT02819635] and U‑ACCOMPLISH [NCT03653026]) showed significant improvements in AP, BU, and fatigue following induction with upadacitinib (UPA) in patients with active UC who had previously failed conventional or biologic therapy. We evaluated the effects of 52-week UPA maintenance treatment on AP, BU, and fatigue in patients who achieved a clinical response after induction.
MethodsFour hundred fifty-one patients who achieved a clinical response after 8 weeks of induction with UPA 45 mg once daily (QD) were enrolled in the U-ACHIEVE maintenance study and were re-randomised 1:1:1 to UPA 15 mg QD (n=148), UPA 30 mg QD (n=154), or placebo (PBO) QD (n=149). Endpoints in this analysis were the percentage of patients who reported no AP or no BU at Weeks 0, 4, 8, 20, 28, 36 and 52, respectively, and the change in Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue (FACIT–F) from induction baseline to Weeks 0 and 52 in the maintenance study. Patients recorded AP and BU daily via an electronic, handheld device. Lastly, the percentage of patients reporting a clinically meaningful within person change (MWPC), defined as ≥5-point increase in FACIT-F score from induction baseline, and normalization of fatigue, defined as a FACIT-F score >40 points, were determined at Weeks 0 and 52.
ResultsSignificantly more patients reported no AP at Week 8 for UPA 15 mg vs PBO (60.8% vs 48.3%, p<0.05, Figure 1) and at Week 12 for UPA 30 mg vs PBO (59.7% vs 43.6%, p<0.01); significant differences were maintained through Week 52 (15 mg: 45.9%; 30 mg: 55.3% vs PBO: 20.8%, p<0.001). For no BU reported, significant differences vs PBO were observed with UPA 30 mg at Week 4 (68.8% vs 54.4%, p<0.05, Figure 2) and with UPA 15 mg at Week 8 (64.9% vs 49.7%, p<0.01) and were maintained through Week 52 (15 mg: 56.1%; 30 mg: 63.6% vs PBO: 17.4%, p<0.001). A significantly greater percentage of patients achieved MWPC in FACIT-F with both UPA 15 mg (55.4%) and UPA 30 mg (58.8%) compared with PBO (35.1%; p<0.001) at Week 52. In addition, a greater percentage of UPA-treated patients achieved normalization of fatigue (52.0% and 55.7% for UPA 15 mg and UPA 30 mg, respectively) vs PBO (35.7%) at Week 52 (p<0.01).
ConclusionIn patients with moderately to severely active UC who responded to UPA 45 mg induction treatment, significant and clinically meaningful improvements in patient-reported AP, BU, and fatigue achieved during induction were sustained through 52 weeks of UPA 15 mg or 30 mg maintenance treatment.


The QUASAR Induction Study 1 (NCT04033445) is a phase 2b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of guselkumab (GUS), an interleukin-23 p19 subunit antagonist, as induction therapy in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) who had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional (ie, thiopurines or corticosteroids) or advanced therapy (ie, tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists, vedolizumab, or tofacitinib).
MethodsPatients included in these analyses had moderately to severely active UC (defined as a modified Mayo score of 5 to 9, inclusive) with a Mayo rectal bleeding subscore ≥ 1 and a Mayo endoscopy subscore ≥ 2 obtained during central review of video endoscopy at baseline. Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive IV GUS 200 mg, 400 mg, or placebo at Weeks 0, 4, and 8. The primary endpoint was clinical response at Week 12, and major secondary endpoints included clinical remission, symptomatic remission, endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic mucosal improvement, and endoscopic normalization at Week 12. Type 1 error was controlled at the 0.05 significance level for the primary endpoint; no other endpoints were controlled for multiplicity. Safety was assessed through Week 12.
ResultsThree hundred thirteen patients were randomized in the primary analysis population (mean age, 41.6 yrs; male 59.1%, mean UC duration, 7.55 yrs; mean Mayo score, 9.2; endoscopy subscore of 3 indicating severe disease, 70%; baseline oral corticosteroid use, 39.6%). Approximately 50% had a prior inadequate response or intolerance to advanced therapy for UC. The baseline demographics and disease characteristics were generally similar among treatment groups (Table 1). At Week 12, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with GUS 200 mg and 400 mg achieved clinical response compared with placebo (61.4% and 60.7% vs 27.6%, respectively, both p<0.001). A greater proportion of GUS-treated patients compared with placebo-treated patients achieved the major secondary endpoints at Week 12 (Figure 1). The proportions of patients reporting adverse events, serious adverse events, and adverse events leading to discontinuation in the GUS groups were not greater compared with placebo (Table 2). No serious infections were reported for GUS. No cases of malignancy or death were reported.

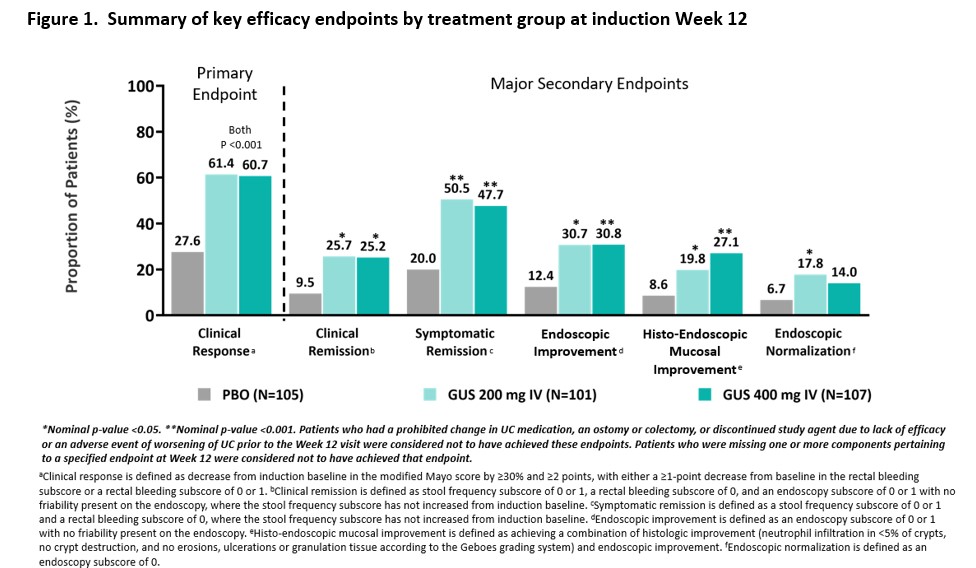
 Conclusion
ConclusionIn patients with moderately to severely active UC, GUS induction treatment demonstrated superior efficacy compared with placebo treatment. Overall, safety results through Week 12 were consistent with the known safety profile of GUS in approved indications. The efficacy and safety of GUS 200 mg and 400 mg were comparable.
Background
Endoscopic and histologic activity are important therapeutic targets in ulcerative colitis (UC). The Paddington International Virtual ChromoendoScopy ScOre (VCE-PICaSSO)1 demonstrated that enhanced visualisation of subtle mucosal and vascular inflammatory changes correlated strongly with histology. However, without adequate training, the subjective evaluation of white light (WL) and VCE endoscopic scores varies between observers. We aimed to develop an artificial intelligence (AI) system for objective assessment of endoscopic disease activity and predict histology related to both white light and VCE videos.
MethodsMethods
469 endoscopy videos (48512 frames) from 235 patients representative of all grades of inflammation, from our prospective PICaSSO multicentre study1 were used to develop a convolutional neural network (CNN). 316 videos were divided into training (254) and validation (62) sets. 153 additional videos (78 patients) were used as test cohort. The videos were edited to separate clips with WL and with VCE, and assessed using Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity (UCEIS) and PICaSSO, respectively. The classification stage of a pre-trained ResNet50 CNN classifier was trained to predict the healing or active inflammation on video frames. One network was trained to predict endoscopic remission (ER) as UCEIS≤1 from WL frames, and a second network was trained to predict PICaSSO≤3 from VCE. Histological remission (HR) was defined as Robarts Histological Index (RHI) ≤3 with no neutrophils in lamina propria or epithelium.
ResultsResults
In the validation cohort, our system predicted ER (UCEIS ≤1) in WL videos with 82% sensitivity (Se), 94% specificity (Sp) and an area under the ROC curve (AUROC) of 0.92. For the detection of remission in VCE videos (PICaSSO ≤3) Se was 74%, Sp 95%, and AUROC 0.95. In the testing cohort of independent videos, the diagnostic performance for both cut offs of ER remained similar. Table 1
Our system also had an excellent diagnostic performance for the prediction of HR in the validation set, with Se, Sp, and Accuracy of 92%, 83%, and 85% respectively, using VCE, and 83%, 87%, and 86% respectively, with WL. In the testing set performance declined modestly while remaining good. Of note, the algorithm’s prediction of histology was similar with VCE and WL videos. Table 2


Conclusions
Our AI system accurately recognize endoscopic remission in videos and predict histological remission equally well. This is the first AI model developed to analyse inflammation and endoscopic remission in VCE through the PICaSSO score, and the first multi-domain system providing a complete endoscopic and histologic assessment.
Reference
1. Iacucci et al. Gastroenterology 2021
1) To review the clinical key predictors of poor outcome in IBD
2. To understand the progress made in predicting the future for a given IBD patient
3. To learn how to communicate risk to the patient
IBD is a chronic immune-mediated disease that requires continuous patient care. The frequent contact and the good relationship with the multidisciplinary team (MDT) are essential for improving quality of life (QoL) and medication adherence aiming at treatment success. The aim of the study was to assess the importance of MDT in the view of patients with IBD and its impact on QoL and in medication adherence.
MethodsA cross-sectional study was carried out, including 114 patients from an IBD reference center in Brazil. The relevance of MDT was assessed through a questionnaire that included the importance of physicians, nurses, nutritionists and psychologists in the patient care. QoL was assessed by IBDQ. Treatment adherence and knowledge about the disease were assessed using the Morisky and CCKNOW questionnaires, respectively.
Results: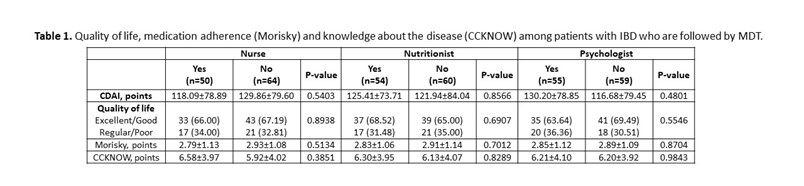 In total, 69 (60.53%) patients with CD and 45 (39.47%) patients with UC were included. The mean age was 39.16 (±13.50) years and 58.77% were female. The disease duration was 9.88 (±7.35) years. Presence of comorbidities was observed in 52.63% patients. About 57 (82.61%) patients with CD use biological therapy, with a statistical difference (p <0.0001) when compared to patients with UC (37.78%). The gastroenterologist was considered very important by 91.23% of patients, coloproctologist by 62.07% of patients, nurse by 65.05% of patients, nutritionist by 50% of patients and psychologist by 47.25% of patients. In the analysis of QoL, 24 (21.05%) patients had excellent QoL, 52 (45.61%) had good QoL, 29 (25.44%) had regular QoL and 9 (7.89%) had poor QoL, with no difference between patients who followed with nurses or other MDT professionals (Table 1). Medication adherence was low in 58.88% of patients. Knowledge about the disease was low (6.21 ± 3.99 points), being higher among patients with CD (p = 0.01). Patients identify the doctor as the main provider of care for their health, but about 10% leave with doubts from their appointments. 10% of patients think that more care with the nurse is necessary and less than 10% of patients are clarified by the nurse about QoL, ostomies, fecal incontinence, disease activity, biological therapy and sexuality.
In total, 69 (60.53%) patients with CD and 45 (39.47%) patients with UC were included. The mean age was 39.16 (±13.50) years and 58.77% were female. The disease duration was 9.88 (±7.35) years. Presence of comorbidities was observed in 52.63% patients. About 57 (82.61%) patients with CD use biological therapy, with a statistical difference (p <0.0001) when compared to patients with UC (37.78%). The gastroenterologist was considered very important by 91.23% of patients, coloproctologist by 62.07% of patients, nurse by 65.05% of patients, nutritionist by 50% of patients and psychologist by 47.25% of patients. In the analysis of QoL, 24 (21.05%) patients had excellent QoL, 52 (45.61%) had good QoL, 29 (25.44%) had regular QoL and 9 (7.89%) had poor QoL, with no difference between patients who followed with nurses or other MDT professionals (Table 1). Medication adherence was low in 58.88% of patients. Knowledge about the disease was low (6.21 ± 3.99 points), being higher among patients with CD (p = 0.01). Patients identify the doctor as the main provider of care for their health, but about 10% leave with doubts from their appointments. 10% of patients think that more care with the nurse is necessary and less than 10% of patients are clarified by the nurse about QoL, ostomies, fecal incontinence, disease activity, biological therapy and sexuality.
Patients considered doctors as the most important professionals in their care. Although the service has a multidisciplinary team, not all patients had the opportunity to consult with all professionals, mainly do the Covid pandemic in 2020 and 2021. The lack of contact with the entire team, especially with the nurse, may have contributed to low medication adherence and low knowledge of the disease, impacting disease control and QoL.
Data regarding the influence of prednisolone tapering on clinical outcomes among patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) are limited. We aimed to investigate the influence of different prednisolone tapering algorithms on the effectiveness of infliximab (IFX) among patients with UC.
MethodsThis Danish retrospective single-center study included all patients with UC who were treated with IFX between 2009 and 2019 at Herlev University Hospital. The patients were grouped according to the prednisolone tapering: standard (≤5 mg/week), fast (>5 mg/week), or direct discontinuation after an initial course of less than one week. Finally, we included a control group of patients treated with IFX monotherapy. The primary outcome was corticosteroid-free clinical remission at weeks 14 and 52 defined as a partial Mayo score ≤1. Variables with a p-value ≤0.20 in univariable regression analysis were included in multivariable analysis. A subgroup analysis containing patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis (ASUC) treated with at least 40 mg of prednisolone at initiation of IFX was performed.
The study included 148 patients with UC of whom 81 (54.7%) were treated with prednisolone at the initiation of IFX. No association between prednisolone tapering and corticosteroid-free clinical remission with IFX at weeks 14 or 52 was observed (Figure 1 and Table 2). However, a higher proportion of patients in the standard tapering group achieved a C-reactive protein (CRP) level less than 5 mg/L at week 14 as compared with the fast-tapering group (23/23 (100%) vs. 14/18 (77.8%); p=0.03) and directly discontinuation group (6/10 (60%); p=0.03). This difference was not explained by prednisolone usage. In addition, none of the patients within the standard tapering regime (0/24; 0%) had severe activity at week 14 whereas this was seen in 4/19 (21.1%) in the fast tapering regime (p=0.03). In the subgroup analysis of 33 patients with ASUC, the standard tapering algorithm was associated with higher clinical remission as compared with the fast tapering regime at week 14 (9/14 (64.3%) vs. 5/19 (27.8%); p=0.02) and clinical response or remission at week 52 (12/14 (85.7%) vs. 7/19 (36.8%); p=0.01, Figure 2).
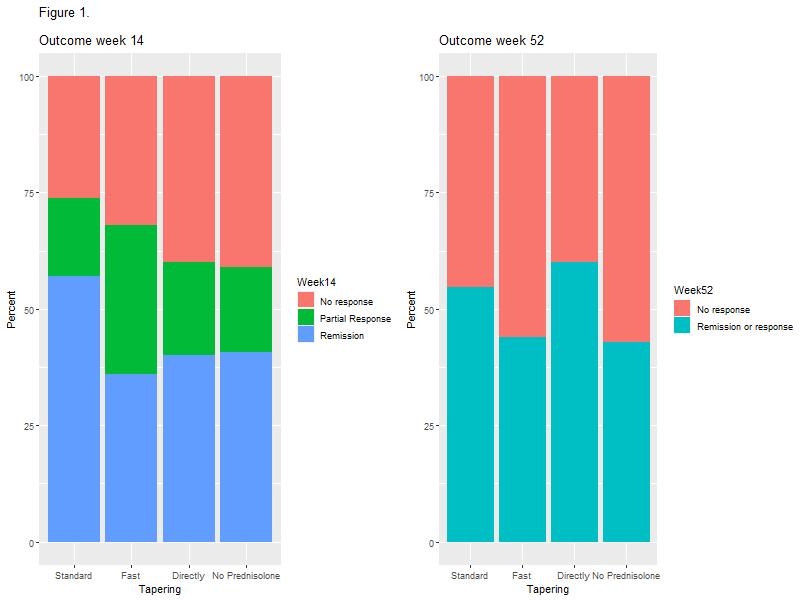
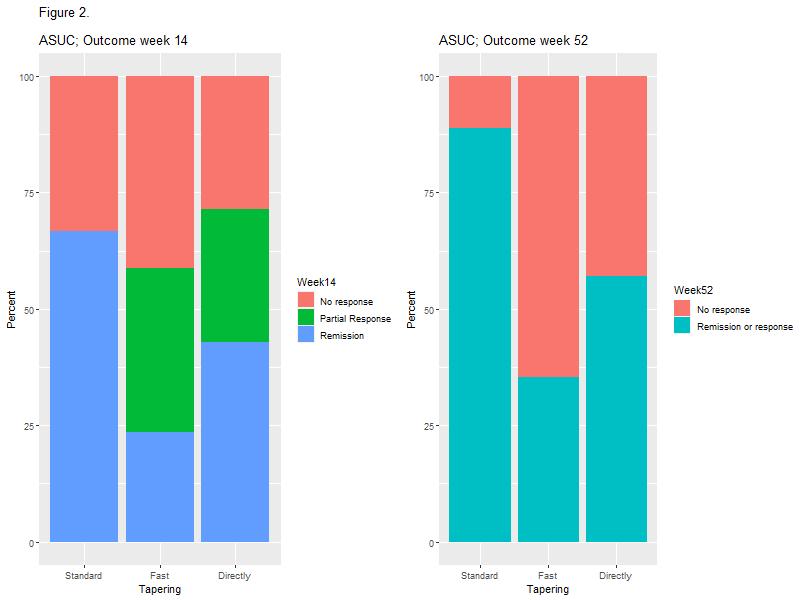
This study demonstrated no overall impact of prednisolone tapering algorithms on short and long-term effectiveness of IFX in patients with UC. However, standard tapering resulted in lower CRP levels and fewer cases of severe disease activity in the overall cohort and higher rate of short and long-term clinical response among ASUC patients, as compared with fast tapering regimes. Taken together, the data indicate that longer corticosteroid exposure in patients with high disease burden might improve IFX responses.
Educational objectives:
- To discuss the therapeutic options for paediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refractory to standard medical therapy
- To review the current evidence for segmental resection for patients with Crohn’s disease (CD)
- To review the evidence for “out of the box” treatments such as tacrolimus for both diseases, thalidomide for CD, granulocyte- monocyte apheresis, fecal microbial transplantation, mesenchymal stromal or adipose cell therapy for refractory perianal fistulas, dual biologics and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Presentation outline:
When patients with IBD fail standard medical therapies there are limited therapeutic options. The first step should be to optimize biologic therapy (based on therapeutic drug monitoring in anti-TNF treated patients or empiric escalation in patients treated with vedolizumab or ustekinumab). Tofacitinib should be considered for patients with ulcerative colitis (UC).
Surgical resection has an established benefit in segmental CD even in the colon.
The edition of nutritional therapy as a combination treatment with biologics may be considered for selected cases.
Tacrolimus was shown efficacious in UC and may serve as a bridge to other therapies such as vedolizumab or even in combination at low doses with vedolizumab.
Thalidomide was studies in CD but treatment is limited by adverse events in high rate and rarely sustainable.
Granulocyte- monocyte apheresis has a limited effect (mainly in UC). Fecal microbial transplantation has emerged a promising treatment with negligible side effects. However, studies using different techniques have yielded limited short-term benefit only.
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant is regarded as a “last resort” option for patients with refractory CD but was studied so far only in adults with promising results though carrying a very high rate of adverse events.
Finally, in the last 2-3 years evidence accumulate on combination of different biologics. Though expensive, such combination may provide relief in refractory cases but more research is needed.
Direct health care costs have shifted towards drug-related expenditures in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Frequently, patients will have to switch to a second- or third-line biological therapy due to no response or loss of response. The aim of this study was to describe the use and efficacy of biological therapy in a tertiary centre during a 10-year period and investigate the need for surgery.
The study population consisted of all bio-naïve IBD patients who initiated biological therapy between January 1, 2010 and February 19, 2020 at the Gastro unit, Hvidovre Hospital, Denmark. The electronic medical records were reviewed, and data were systematically registered. Failure of the biological therapy as no response and loss of response was defined by the need for surgery, steroid or shift in biological therapy.
ResultsThe study population consisted of 291 (46.9%) patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), 327 (52.7%) with Crohn’s disease (CD) and 3 with (0.5%) IBD Unclassified (IBDU), who initiated biological therapy with a median follow-up of 3 (IQR=2-5) years from initiation of therapy. The annual number of patients who initiated biological therapy was increasing throughout the study period.
Most patients (457, 73.6%) received one biological drug, 126 (20.3%) received two, and 38 (6.1%) received three or more different types of biological drugs during the study period. Systemic steroid was required in 99 patients (15.9%) and the 5-year surgery-free survival was 76.5% (120 patients with surgery). 302 patients (54.3%) had effect of the first biological therapy at one year follow-up.
In multivariate Cox-regression analyses, concurrent treatment with thiopurines decreased the risk of failure of the first biological therapy in UC patients (hazard ratio (HR) 0.745, 95% CI: 0.559-0.992) but not in CD patients (HR 0.969, 95% CI: 0.722-1.300). Male gender decreased the risk of failure (HR: 0.677, 95% CI: 0.505-0.908) while higher age at initiation of biological therapy increased the risk (HR: 1.0152, 95% CI: 1.004-1.027) in CD patients. These factors had no impact in UC patients. Prior surgery, disease duration and location were not associated with increased risk of failure of first biological therapy.

In conclusion, an increasing number of IBD patients received biological therapy during the 10-year period at our tertiary centre. A considerable part of IBD patients in biological therapy will require surgery, additional steroids, or second line biological therapy. Our findings suggest a beneficial role of thiopurine in combination with biological therapy. Improved identification of patients not responding to first line biological therapy is of great importance.


