1. To understand the opportunities of virtual clinics for both patients and healthcare professionals
2. To get practical examples from two countries of how to implement virtual clinics
3. To get some advice of what to consider and prepare for concerning virtual clinics
4. To hear the patients opinion about virtual clinics
Chronic abdominal pain is highly prevalent in IBD patients in remission. The aetiology is incompletely understood, although persistent histologic inflammation, post-inflammatory visceral hypersensitivity, and altered gut-brain interaction are believed to contribute. Data on the characteristics of IBD patients suffering from chronic abdominal pain are sparse, yet essential for the identification of treatment targets. We investigated clinical, lifestyle and psychosocial factors associated with chronic abdominal pain in a real-world cohort of IBD patients in remission.
MethodsA prospective multicentre study was performed enrolling consecutive IBD patients, between Jan 1, 2020 and Jul 1, 2021, using myIBDcoach, an established remote monitoring platform for IBD. Patient reported outcome measures on disease activity, lifestyle and psychosocial factors (i.e. depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress, and life events) were assessed in three-monthly intervals. Chronic abdominal pain in IBD in remission (IBDremissionPain+) was defined as an abdominal pain score ≥3 (1-10 numeric rating scale (NRS)) at ≥1/3 of all assessments combined with faecal calprotectin <150 μg/g in 90 days around periodic assessments. Multivariable logistic regression, adjusting for relevant confounders, was performed to identify risk factors for IBDremissionPain+ compared to patients in remission without chronic abdominal pain (IBDremissionPain-).
ResultsIn total, 559 patients were followed prospectively, of which 429 (76.7%) were in biochemical remission. Of these, 198 (46.2%) fulfilled the criteria for chronic abdominal pain. IBDremissionPain+ patients were characterized by female sex, higher BMI, and shorter disease duration compared to IBDremissionPain- (Table 1). IBDremissionPain+ patients reported significantly higher levels of stress, fatigue, depressive and anxiety symptoms, and occurrence of life events (Table 2). On multivariable logistic regression, female sex (aOR 2.58), shorter disease duration (<10years, aOR 2.31), higher BMI (aOR 1.06), higher levels of stress (aOR 1.19), fatigue (aOR 4.73), and life events (aOR 1.65) were all significantly associated with chronic abdominal pain (Table 3). The univariable association between pain and anxiety and depressive symptoms was modulated by stress in the multivariable analysis.


In this real-world population of IBD patients in remission, 46.2% experience chronic abdominal pain, characterized by female sex, shorter disease duration, higher BMI, fatigue and psychosocial factors. The gut-brain interaction in this population is represented by higher levels of depressive and anxiety symptoms, but the relation to abdominal pain is potentially modulated through increased levels of perceived stress.
Perianal fistulising Crohn’s disease (CD) is an aggressive disease phenotype that can have a significant impact on patients’ quality of life. Current biological understanding of perianal fistulising CD remains inadequate and previous classification systems have not provided clear guidance on therapy in clinical practice nor on defining patient cohorts within clinical trials. To counter this unmet need, we propose a new classification system for perianal fistulising CD.
The proposed classification system was developed through a modified nominal group technique expert consensus process involving open discussion and formal voting on previously defined statements. Consensus agreement was defined a priori as 80% voting “strongly agree” or “agree with minor reservation”. Participants included gastroenterologists, radiologists, surgeons active in a tertiary IBD centre and a patient representative.
ResultsThe classification identifies four groups of patients with perianal fistulising CD. Key elements include stratification according to disease severity as well as disease outcome; synchronisation of patient and clinician goals in decision making, with a proactive, combined medical and surgical approach, on a ‘treat to patient goal' basis; and identification of indications for curative fistula treatment, diverting ostomy and proctectomy. The new classification retains an element of flexibility, in which patients can cycle through different classes over time. Furthermore, with each specific class comes a paired treatment strategy suggestion and description of clinical trial suitability.
The proposed classification system is the first of its kind and is an important step towards tailored standardisation of clinical practice and research in patients with perianal fistulising CD.
GALAXI 1 is a Phase 2, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled, multicenter study evaluating efficacy/safety of guselkumab (GUS), a selective IL-23 p19 antagonist, in patients (pts) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD) with inadequate response/intolerance to conventional therapies (corticosteroids, immunomodulators) and/or biologics (tumor necrosis factor antagonists, vedolizumab). At Week (Wk) 12, all GUS induction doses (200, 600, and 1200mg IV) had greater improvements vs PBO for key clinical/endoscopic outcomes. We report clinical efficacy and safety of maintenance treatment through Wk48.
MethodsGALAXI employed a treat-through design over 48 wks. In induction pts were randomized to GUS 200, 600, or 1200mg IV, ustekinumab (UST) ~6mg/kg IV, or PBO IV. Pts transitioned to maintenance dosing as follows: PBO non-responders to UST ~6mg/kg IV to 90mg SC q8w, PBO responders to PBO SC q4w, GUS 200mg IV to 100mg SC q8w, GUS 600mg IV to 200mg SC q4w, GUS 1200mg IV to 200mg SC q4w, and UST ~6mg/kg IV to 90mg SC q8w. Pts randomized to PBO were not included in Wk48 efficacy analyses. Primary and major secondary endpoints evaluated efficacy of GUS vs PBO at Wk12. Evaluations of Wk48 endpoints were prespecified but not multiplicity controlled. UST was a reference arm; the study was not powered to evaluate differences between treatment groups with respect to efficacy at Wk48.
ResultsThrough Wk48, 248 pts in the primary efficacy analysis set were randomized and evaluated. Baseline demographics were similar across groups (Table 1). Discontinuation rates were low across active treatment groups.No dose response was observed across clinical efficacy assessments (Table 2). Proportions of pts achieving clinical remission at Wk48 ranged from 57.4-73.0% among GUS dose groups. The vast majority of pts in clinical remission were also in corticosteroid-free remission at Wk48; with rates ranging from 55.7-71.4% among GUS dose groups. PRO-2 remission rates ranged from 50.8-69.8%, and proportions of pts achieving clinical response ranged from 67.2-84.1% among GUS dose groups. Proportions of pts achieving abdominal pain scores ≤1 or daily average number of liquid or very soft stools ≤3 are presented in Table 2. Outcomes in the reference UST group are also shown in Table 2.
Key safety event rates were similar among GUS dose groups (Table 3); no opportunistic infections, cases of tuberculosis, or deaths were reported in any group.


In this treat-through Phase 2 study of pts with moderately to severely active CD, GUS was safe and effective. GUS induction followed by SC maintenance achieved high rates of clinical efficacy at Wk48. Safety results were consistent with the known safety profile in approved indications.
The impact of COVID-19 has been of great concern in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) worldwide, including an increased risk of severe outcomes and/or possible flare of IBD. This study aims to evaluate prevalence, outcomes, the impact of COVID-19 in patients with IBD, and risk factors associated with severe COVID-19 or flare of IBD activity.
MethodsA consecutive cohort of IBD patients followed at the McGill University Health Care Centre diagnosed with COVID-19 infection was obtained between March 1, 2020, and April 30, 2021. Demographics, comorbidities, IBD (type, treatments, pre-and post-COVID clinical activity, biomarkers, and endoscopic activity), and COVID-related outcomes (pneumonia, hospitalization, death, and flare of IBD disease) were analyzed.
ResultsA total of 3,516 IBD cohort patients were included. 82 patients (2.3%) were diagnosed with COVID-19 infection (median age 39.0 (IQR 27.8-48.0), 77% with Crohn’s disease, 50% were female). The prevalence of COVID infection in IBD was significantly lower compared to the general population in Canada and Quebec (3.5% vs. 4.3%, p<0.001). Severe COVID occurred in 6 patients (7.3%); 2 patients (2.4%) died. A flare of IBD post-COVID infection was reported in 8 patients (9.8%) within 3 months. Biologic therapy was held during active COVID infection in 37% of patients. Age ≥55 years (odds ratio (OR):11.1, 95%CI:1.8–68.0), systemic corticosteroid use (OR:4.6, 95%CI:0.7-30.1), active IBD (OR:3.8, 95%CI:0.7-20.8) and comorbidity (OR:4.9, 95%CI:0.8-28.6) were factors associated with severe COVID. After initial infection, 61% of IBD patients received COVID-19 vaccinations.

 Conclusion
ConclusionThe prevalence of COVID-19 infection among patients with IBD was lower than that in the general population in Canada. Severe COVID, mortality, and flare of IBD were relatively rare, while a large proportion of patients received COVID vaccination. Older age, comorbidities, active IBD disease, and systemic corticosteroid, but not immunosuppressive or biological therapy were associated with severe COVID infection.
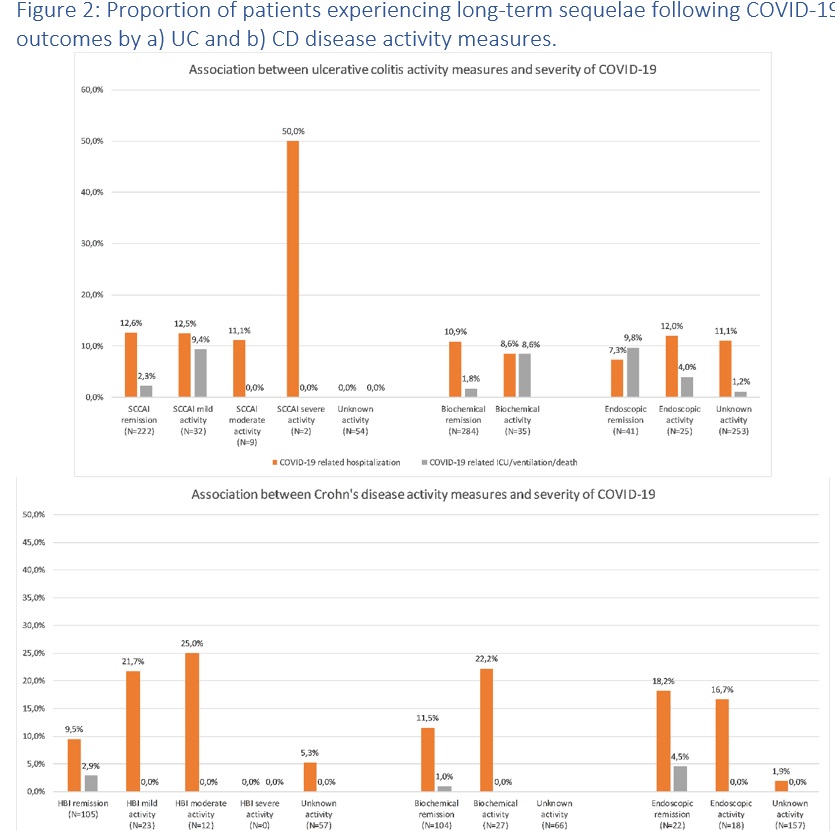
Whether the disease activity of ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) is correlated with the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains poorly investigated with only few selected cohort studies having addressed this in the past.
MethodsWe conducted a population-based study investigating the outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with UC and CD in Denmark. The Danish COVID-19 IBD Database is an extensive population-based database which prospectively monitors the disease course of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 among patients with UC and CD. Severe COVID-19 was defined as COVID-19 necessitating intensive care unit admission, ventilator use, or death, while adverse COVID-19 was defined as requirement of COVID-19 related hospitalization. Clinical disease activity was measured by simple clinical colitis index and Harvey-Bradshaw Index in UC and CD, respectively. The biochemical activity was defined as C-reactive protein higher than 5 mg/L or fecal calprotectin higher than 250 μg/g. The endoscopic activity was defined as Mayo Endoscopic Subscore of at least 2 in UC, or Simple Endoscopic Score Crohn’s Disease of at least 3 for CD. Sequelae following COVID-19 were defined as symptoms that (i) developed during or after an infection consistent with COVID-19, (ii) and were present for more than 12 weeks, (iii) and were not attributable to alternative diagnoses.
ResultsDuring the inclusion period between January 28th, 2020, to April 1st, 2021, the study included 319 patients with UC and 197 patients with CD who developed laboratory confirmed COVID-19. Of these, data on clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic activity were available among 265/319 (83.1%), 319/319 (100.0%), and 66/319 (20.7%) of patients with UC, respectively, and 140/197 (71.1%), 131/197 (66.5%), and 42/197 (21.3%) of patients with CD. Figures 1-2 outlines the outcomes of COVID-19 according to the degree of clinical, biochemical and endoscopic disease activity. In both UC and CD, clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic activity were not associated with adverse or severe COVID-19, nor long-term outcomes, in unadjusted nor adjusted analysis (Table 1).


 Conclusion
ConclusionIn this population-based study, we found no association between disease activity of UC or CD and severity of COVID-19. These findings have implications for the risk stratification of patients with IBD acquiring COVID-19.
Educational Objective:
1. To review the indications for standard indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT)
2. To understand the evidence regarding the role of HBOT for the treatment of acute severe ulcerative colitis
3. To understand the evidence regarding the role of HBOT for the treatment of ileoanal pouch complications
4. To review the practicalities and limitations of HBOT
Educational objectives:
1. To understand why combination therapy is being considered?
2. To review what we have learned from the past, when combination works
3. To review what we have learned from the past, when combination does not work
4. To review what we have learned from the past, when combination is bad and dangerous
5. To discuss and review combination therapy in IBD today and tomorrow
Ustekinumab (UST) and vedolizumab (VDZ) are widely used to treat patients with Crohn’s disease (CD). However, limited data exist regarding comparative effectiveness of these agents for patients with CD who have failed anti-TNF treatment. We aimed to compare the efficacy of UST and VDZ utilizing the largest cohort of CD patients who failed anti-TNF in real world clinical practice.
MethodsWe conducted a retrospective cohort analysis using data retrieved from the UK IBD BioResource, capturing 34,148 subjects. We identified patients with CD, who failed anti-TNF and were subsequently treated with UST or VDZ as second or third-line therapy. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was used to balance groups using a propensity score-weighting approach accounting for baseline patient or disease related characteristics. Persistence on therapy with clinician assessment of treatment success, without the need for treatment change or surgery was used to estimate the response to treatment. We compared treatment survival curves before and after IPTW and used a log rank test for differences between groups
Results654 CD patients received VDZ, either as second line (51%) or third line (49%) therapy. 365 patients received UST, 52% as a second line and 48% as a third line therapy. All patients received either infliximab or adalimumab as first and/or second biologic therapy. Baseline characteristics are detailed in table 1. Following IPTW, variables were well balanced. Patients receiving VDZ showed similar rates of treatment success compared to UST as second- and third-line biologic agent after anti TNF failure (before IPTW adjustment, log rank p 0.241; after IPTW, log rank p 0.154). Outcomes for UST were similar between 2nd and 3rd line usage (p 0.81), but outcomes for VDZ were significantly worse when used 3rd line compared to 2nd line (p <0.0001).Subgroup analysis of unadjusted survival data showed significantly better outcomes for patients with ileal disease distributiontreated with UST compared to VDZ (p=0.043) but no significant differences in outcomes for subgroups with colonic or ileocolonic disease.We estimate persistence on UST and VDZ to be 67%, 54%, 49% and 49% at 1, 2, 3 and 5 years respectively.
ConclusionUsing data from a multi-institutional cohort of patients with CD with larger number of participants and longer follow-up than previous cohorts, we demonstrate no difference between UST and VDZ used as second and/or third line biologic therapy, after anti-TNF failure. Subgroup analysis reveals some patient characteristics predictive of differential treatment response.


We compared the efficacy of adalimumab, infliximab, ustekinumab, and vedolizumab for achieving endoscopic healing (EH) in the ileum and colon after one-year of therapy in Crohn’s disease (CD).
MethodsA pooled analysis of patient-level data from 344 patients with CD from four clinical trial programs was performed. Patients who received continuous adalimumab, infliximab, ustekinumab, or vedolizumab throughout the trial and had at least one ileocolonic segment with a Simple Endoscopic Score for CD (SES-CD) ≥ 3 at enrolment were included. Proportions of patients achieving one-year endoscopic healing (EH), defined as SES-CD of 0, using each of four biologics were compared. Multivariate logistic regression was used to model the relationship between individual biologics and one-year outcomes, adjusted for potential confounders of EH, including disease duration, concomitant corticosteroid use, and prior anti-TNF failure.
ResultsCompared to vedolizumab [10/77 (13%)], both infliximab [29/79 (36.7%), aOR: 3.27 (95% CI: 1.34-8.01), p<0.001] and adalimumab [12/40 (30%), aOR: 3.01 (95% CI: 1.10-8.21), p=0.032] were superior for achieving one-year EH of the ileum among patients with ileal involvement at baseline. No difference was observed between ustekinumab [5/22 (22.7%)] and vedolizumab [aOR: 2.75 (95% CI: 0.76-9.91), p=0.123]. In biologic-naïve patients, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab were superior to vedolizumab for achieving one-year EH of the ileum. For colonic disease, in comparison to ustekinumab [9/31 (29.0%), adalimumab [30/48 (62.5%), aOR: 4.04 (95% CI: 1.88-8.71), p<0.001] and infliximab (55/105 (52.4%), aOR: 2.02 (95% CI: 1.03-3.99), p=0.041] were superior for one-year EH in the colon among patients with colonic involvements at baseline. No difference was seen between vedolizumab [26/87 (29.9%)] and ustekinumab [aOR: 1.01 (95% CI: 0.39-2.59), p=0.987]. Similar differences were noted among biologic-naïve patients.


 Conclusion
ConclusionIn this post-hoc analysis of pivotal clinical trials, TNFα antagonists were generally superior to vedolizumab and ustekinumab for achieving EH of the ileum and colon in patients with CD. However, among biologic-naïve patients, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab were superior to vedolizumab for attaining one-year EH of the ileum.
To gain insight into vedolizumab (VDZ) use as a first-line biologic in Crohn´s Disease (CD), this real-world study aimed to assess, within the maintenance phase, the 1-year comparative effectiveness and persistence of VDZ vs anti-TNF therapy in biologic-naïve CD-patients.
Between 2017-2020, 1200 consecutively enrolled biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and CD were prospectively included in the VEDOIBD-Registry from 45 IBD-experienced centres across Germany. 294 biologic-naïve CD-patients starting a new therapy with VDZ or anti-TNF (adalimumab: ADA or infliximab: IFX) were included in this real-world evidence (RWE) study. The Kaplan-Meier was used to summarize the treatment persistence from the start of therapy through week-52. The primary outcome was week-52 clinical remission (HBI ≤ 4). Patients were analyzed on a modified intent-to-treat basis (mITT; switchers considered as outcome failure) and on a per-protocol (PP) basis (excluding switchers). To reduce selection bias in the estimation of treatment effects, the inverse probability of treatment weighting propensity score (PS) was implemented. A weighted logistic regression was used to evaluate the effectiveness. The results were reported as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
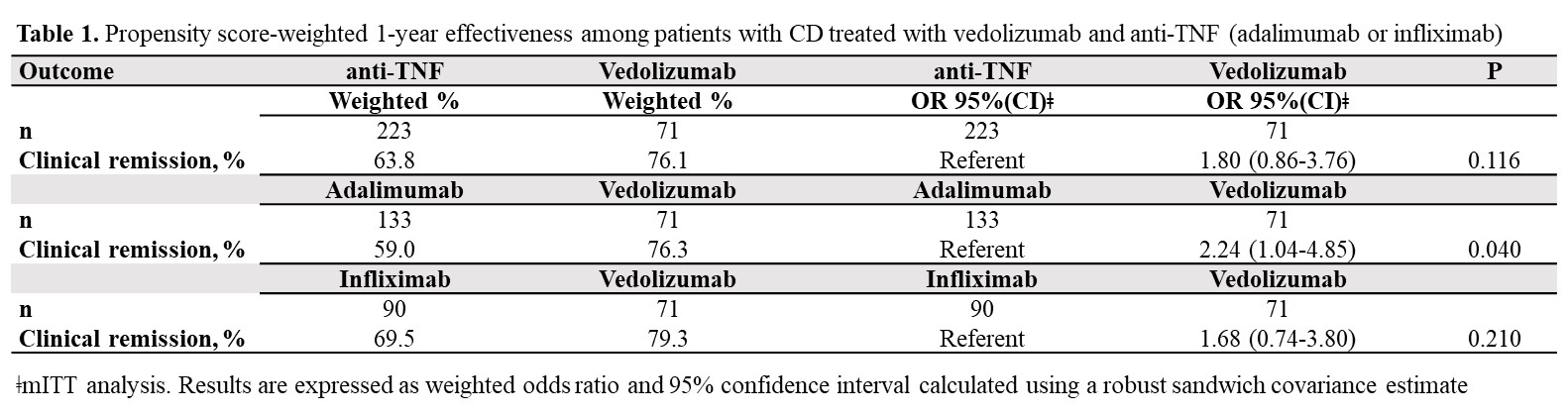
Results71 VDZ and 223 anti-TNF (ADA: 59.6%, IFX: 40.4%) biologic-naïve CD-patients were evaluated. 52-weeks after treatment initiation approximately 94% of VDZ patients were still in continuous treatment vs 75% of ADA and 78% of IFX (Figure 1). The mITT 1-year clinical remission rate was 76.1% for VDZ vs 63.8% for anti-TNF (OR: 1.80, 95% CI: 0.86-3.76). Similar results were observed for VDZ vs IFX (Table 1). In contrast, the clinical remission was significantly higher in the VDZ group than in the ADA group (OR: 2.24, 95% CI: 1.04-4.85). The PP analysis suggested comparative effectiveness, having excluded more anti-TNF switchers. 91.7% of week-14 responders VDZ patients were in clinical remission from week 14 through 52 vs 66.1% of anti-TNF patients (OR: 5.69, 95% CI: 1.66-19.5). Similar, significant, results were observed for VDZ vs ADA and for VDZ vs IFX (Table 2).
ConclusionIn this real-world setting comparing VDZ and anti-TNF in biologic-naïve patients via PS weighted analysis, VDZ showed especially in week-14 responders higher clinical remission rates in comparison to anti-TNF. The higher treatment persistence observed for VDZ, perhaps due to a more favourable safety profile vs anti-TNF, may be considered the main driver for the better effectiveness of VDZ at one year. These findings may aid physicians’ decision-making on the choice of VDZ as the first-line biologic for CD.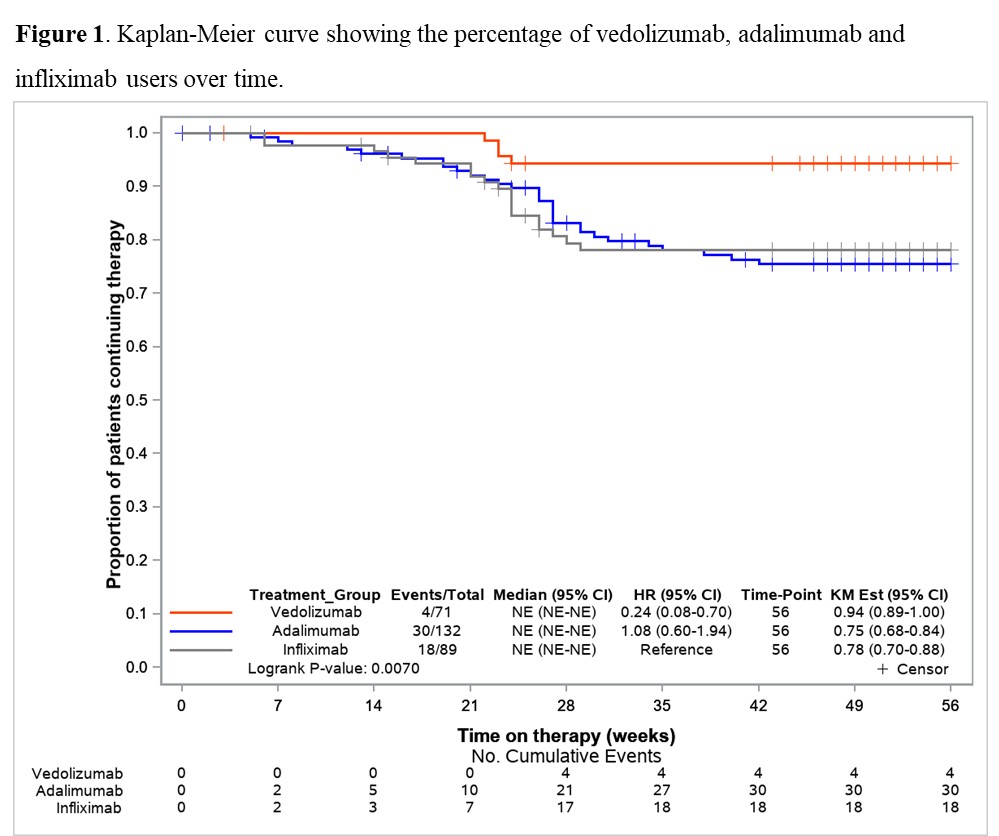

Main aim: To evaluate the retention rate of ustekinumab compared to vedolizumab in Crohn’s disease patients who failed anti-TNF therapy in clinical practice. Secondary aims: To compare the short-term and long-term effectiveness, and the safety of both treatments.
Methods755 patients were included (195 in the vedolizumab cohort and 560 in the ustekinumab cohort). After a median of 20 months (IQR 7.4-30) of follow-up, the survival rate for ustekinumab therapy was higher than vedolizumab (Figure 1). The propensity matching score verified the differences between both therapies. The short-term proportion of patients on clinical remission, steroid-free remission and clinical response was also superior in the ustekinumab cohort (Figure 2). In the long-term, significant differences were observed 2 years after the beginning of the treatments, although no differences in clinical response and remission rates were detected in patients who achieved clinical response at week 16 between both cohorts. Vedolizumab was discontinued in 142 patients and ustekinumab in 185, mainly due to primary non-response (52% in the vedolizumab and 58% in the ustekinumab cohort) and loss of response (34% and 25%, respectively) despite the fact that 35% of the patients required intensification. The predictive factors associated to the discontinuation of the therapy are described in table 1. Adverse events were observed, overall, in 12% of the patients, without differences between both groups (Table 2). Following the discontinuation of the treatment with vedolizumab/ustekinumab, other biologic agents were prescribed in 56% of the patients, and 27% underwent surgery.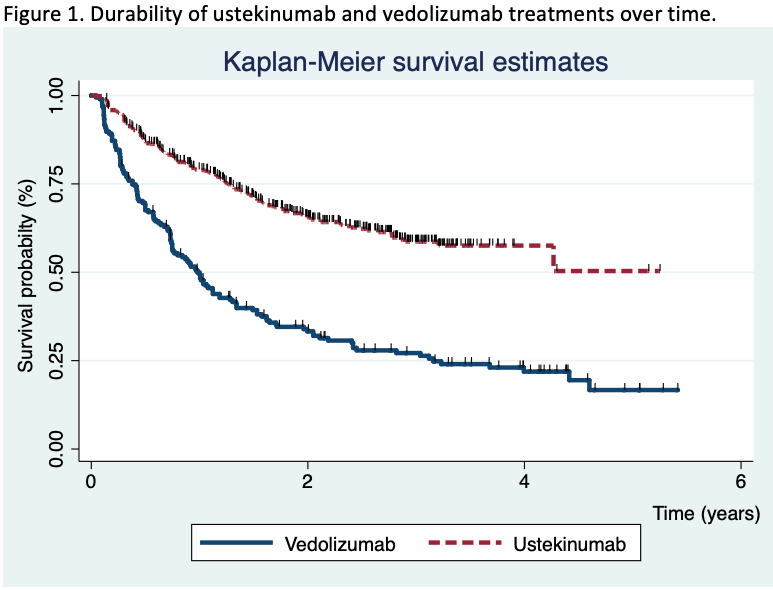



In clinical practice, a relatively high proportion of Crohn’s disease patients who received ustekinumab or vedolizumab for anti-TNF failure, maintained these drugs in the medium-long term, although ustekinumab retention rate was higher in comparison with vedolizumab.
The modified Rutgeerts' score (mRS) differentiates i2a – lesions confined to the anastomosis – and i2b – neoterminal ileum lesions – categories. Its relevance for therapeutic management of Crohn's disease (CD) patients after ileocolonic resection is still debated. Our objective was to compare the postoperative recurrence (POR) risk in patients with a mRS i2a or i2b score using an individual patient data meta-analysis.
MethodsWe conducted a systematic literature search of Medline, Embase and abstracts from international conferences (until July 2020) to identify all relevant studies reporting the risk of clinical and/or surgical POR and the i2a/i2b status in the year following ileocolonic resection. Initial datasets were obtained from the corresponding authors. Time from endoscopy to clinical and surgical POR was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. The association between time to event and mRS was evaluated using a mixed Cox with centre as the random effect.
ResultsFrom the 17 studies identified, 7 published between 2008 and 2019 (cohort studies, n=4; clinical trials, n=2) corresponding to a total of 400 patients (median (InterQuartileRange) age at surgery 34 (26,47) years; 52% female) were included. In the year following ileocolonic resection, 189 (47%) patients displayed an i2a mRS and 211 (53%) an i2b. In the i2b group, we observed more male patients (56% versus 41%, p=0.01), more patients with previous ileocolonic resection (31% versus 21%, p=0.03) and temporary ileostomy (14% versus 6%, p=0.03) and an immunosuppressant or antiTNF therapy was more frequently initiated after endoscopy (42% versus 26%, p<0.01 and 36% versus 54%, p<0.01, respectively). The risk of clinical POR at 1, 3 and 5 years was 11% [6%-15%], 25% [18%-32%] and 36% [27%-43%] in the i2a group and 9% [5%-13%], 33% [26%-41%] and 47% [39%-56%] in the i2b group (p=0.63, p=0.12, et p=0.05 respectively). No significant difference was observed in terms of time to clinical POR (Hazard Ratio (HR)=1.27; Confidence Interval 95% [0.91,1.76]; p=0.16) (Figure 1) or surgical POR (HR=0.94; CI95% [0.44,2.00]; p=0.87). After exclusion of patients having initiated an immunosuppressant or a biologic in the 3 months after endoscopy (remaining cohort, n=361), no difference was observed in terms of clinical POR (HR=1.29 [0.92,1.80]; p=0.13) or surgical POR (HR=0.85 [0.39,1.84]; p=0.68).
In this individual patient data meta-analysis, no difference is observed between i2a and i2b mRS subcategories in terms of clinical, surgical or endoscopic POR. Limits of the mRS may explain this lack of predictive value.
Learning Objectives - Risks associated with anti-TNF treatments
1. Hypersensitivity reactions
2. Dermatological adverse effects with anti‐TNF therapy
3. Autoimmune‐like disorders
4. Infections and management strategies
5. Malignancy
6. Patients’ selection for anti TNFs vs other biologics
Educational objectives:
- To understand the importance of histological remission in IBD
- To understand the hurdles in the assessment of histological remission in IBD
- To understand the potential of automated histological scoring based on artificial analysis
HMGB1 is a ubiquitously expressed nucleoprotein with proinflammatory functions following cellular release. The protein is passively released during tissue necrosis, acting as a damage-associated molecular pattern, but can also be actively secreted by immune cells. Stool and serum HMGB1 levels have been suggested as markers of both inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) activity and colorectal cancer (CRC) invasiveness, and antibody-mediated HMGB1 neutralization was beneficial in animal models of IBD. We explored context-dependent functions of HMGB1 in the injured intestine using novel experimental mice with cell-specific genetic HMGB1 deficiency.
MethodsTo circumvent the postnatal lethality of global HMGB1 deficiency in animals, we used the Cre-lox system to generate enterocyte-specific (Hmgb1ΔIEC, Villin-Cre) and myeloid cell-specific (Hmgb1ΔLysM, LysM-Cre) HMGB1-knockout mice. Animals were subjected to well-established models of acute (DSS, Citrobacter rodentium) and chronic (AOM+DSS, CD45RBhigh T cell transfer colitis, Apc+/min) intestinal injury, followed by clinical, endoscopic, histological and molecular analysis. HMGB1 expression was assessed in human IBD and CRC specimens.
ResultsIBD and CRC biopsies exhibited high levels of HMGB1 expression in epithelia, immune cells, tumor cells and the peritumoral stroma. HMGB1 deficiency from enterocytes and myeloid cells did not alter Citrobacter- or T cell transfer-induced enterocolitis, when epithelial injury was comparably low. In contrast, Hmgb1ΔIEC mice exhibited aggravated DSS-induced colitis, as evidenced by severe weight loss as well as exacerbated neutrophil- and monocyte-driven mucosal inflammation compared to Hmgb1f/f. Whole tissue RNA sequencing indicated defective cellular proliferation in injured Hmgb1ΔIEC intestines. In the AOM+DSS-model, Hmgb1ΔIEC had a comparable tumor burden to Hmgb1f/f, whereas Hmgb1ΔLysM had significantly fewer and smaller tumors, potentially linked to metabolic alterations in the tumor micromilieu. In the Apc+/min model, enterocyte HMGB1 deficiency effectuated more and larger tumors, whereas leukocyte HMGB1 did not affect tumor load.
ConclusionContrasting antibody-mediated HMGB1 neutralization in animal models of IBD, our findings from genetic HMGB1 deletion studies reveal a critical role of enterocyte HMGB1 in the maintenance of the intestinal barrier during severe colitis. Impaired epithelial regeneration or inefficient local immune cell expansion in Hmgb1ΔIEC may account for the aggravated phenotype. HMGB1 from enterocytes and immune cells context-dependently affect maladaptive intestinal would healing, potentially mediated by cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms that warrant further investigation.
Summary content
1. To understand the differences between risk and prognostic factors2. To describe the different types of outcomes
3. To understand the development process of core outcomes
4. To illustrate how prognostic factors can be applied to influence treatment decisions and modify outcomes
Some studies have shown decreased serological response to vaccination in patients on anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) medications. While the large majority of these patients do seroconvert after vaccination, titers have generally been lower and one study showed reduced neutralizing and inhibitory functions. One real-world population-based study compared found no increased infection rate in anti-TNF treated patients, but infection rates were low. The low event rate mandates exploration in longer-term population-based data. We used the epi-Israeli IBD Research Nucleus (IIRN) database to explore the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination in IBD patients in Israel.
MethodsWe included all IBD patients insured in two of the four Israeli HMOs, covering 35% of the population, by validated algorithms, and selected those who received two doses of Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine. These were matched by date of vaccination ±3 days and demographic variables to non-IBD controls. The primary outcome was incidence of positive COVID-19 PCR following vaccination between December, 2020 to June, 2021.
Results12,640 IBD patients received two vaccine doses; the matched cohort included 4,946 matched pairs (total 9,892 subjects). Mean age was 50.5±16.1 years and median follow-up was 22 weeks (range 4.1-24.4). Fifteen (0.3%) vaccinated IBD patients tested positive compared with 15 (0.3%) vaccinated non-IBD controls (OR=1 [95%CI 0.49-2.05], p=1.0). Patients on anti-TNF and/or corticosteroids did not have a higher incidence of positivity – neither compared to the entire group nor to IBD patients treated with vedolizumab/ustekinumab, even after precise matching for demographics, underlying diseases and IBD severity.
ConclusionIn a large population-based cohort of IBD patients in Israel, vaccine effectiveness was equivalent to non-IBD controls and was not influenced by treatment with anti-TNF or corticosteroids. Notwithstanding previous findings of impaired serological response in anti-TNF treated IBD patients, this real-world large-scale study shows that vaccine protection is robust in IBD patients, including those on immunosuppressive medications.
Robust COVID-19 vaccine-induced antibody (Ab) responses are important for protective anti-viral immunity. Data are urgently needed to determine whether vaccine-induced immunity is impacted by commonly used immunosuppressive drug regimens in IBD.
MethodsWe prospectively recruited 447 adults (90 healthy controls and 357 IBD) at nine UK centres. The IBD study population was established (>12 weeks therapy) on either thiopurine monotherapy (n=78), infliximab (IFX) monotherapy (n=61), thiopurine & IFX combination therapy (n=70), ustekinumab (uste) monotherapy (n=56), vedolizumab (vedo) monotherapy (n=62) or tofacitinib (tofa) monotherapy (n=30). Participants had two doses of either ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, BNT162b2 or mRNA1273 vaccines. The primary outcome was anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike (S1 RBD) Ab concentrations, measured using the Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) Ab assay, 53-92 days after second vaccine dose, in participants without prior infection, adjusted by age & vaccine type. Secondary outcomes included proportions failing to generate protective Ab responses (defined cut-off anti-S concentration 15 U/mL, which correlated with 20% viral neutralization).
ResultsGeometric mean S Ab concentrations (figure 1) were lower in patients treated with IFX (153U/mL;p<0.0001), IFX and thiopurine combination (109U/mL;p<0.0001), tofa (430U/mL;p<0.0001) and uste (561U/mL;p=0.013) compared to controls (1596U/ml). No differences in S Ab concentrations were found between controls and thiopurine monotherapy-treated patients (1020U/mL;p=0.62), nor between controls and vedo-treated patients (944 U/mL;p=0.69). In multivariable modelling (figure 2), lower S Ab concentrations were independently associated with IFX (FC 0.10 [95% CI 0.07-0.14], p<0.0001), tofa (0.36 [95% CI 0.19-0.69],p=0.002) and uste (0.56 [95% CI 0.31-1.00],p=0.049), but not with thiopurine (0.77 [95% CI 0.54-1.11],p=0.17) or vedo (1.01 [95% CI 0.61-1.68],p=0.96). mRNA vaccines (3.67 [95% CI 2.72-4.96],p<0.0001) and older age (0.82 [95% CI 0.73-0.91],p=0.0003) were independently associated with higher & lower S Ab concentrations respectively. Protective Ab responses were generated by all thiopurine monotherapy, vedo, tofa and healthy control participants, but not by 11% of patients on IFX monotherapy, 13% on thiopurine & IFX combination therapy and 4% on uste.

COVID-19 vaccine-induced Ab responses are significantly reduced in patients treated with IFX, or tofa, and to a lesser extent with uste. No significant reduction was seen in vedo or thiopurine monotherapy-treated patients. Our data suggest that 3rd primary or booster vaccine doses for IBD patients might be tailored to an individual’s immunosuppressive treatment.
Financial support was provided as a Research Grant by Pfizer Ltd.
Educational objectives:
1. To understand the mechanisms of action of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in IBD
2. To review current knowledge regarding the application of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in Crohn's Disease
3. To have an overview of potential areas of focus for future research
